Fuses, fuse links, and circuit breakers protect your vehicle’s electrical system from overloading. If electrical parts in your vehicle are not working, the system may have been overloaded causing a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker. Here you will find various information related to automotive fuses – the location of units, fuse box diagrams, fuse layouts, and assignment of the fusible links, circuit breakers, fuses, and relays.
Advertisements
Makes
 Acura
Acura  Alfa Romeo
Alfa Romeo  Audi
Audi  BMW
BMW  Buick
Buick  Cadillac
Cadillac  Chevrolet
Chevrolet  Chrysler
Chrysler  Citroën
Citroën  Daewoo
Daewoo  Dodge
Dodge  Ferrari
Ferrari  Fiat
Fiat  Ford
Ford  GMC
GMC  Honda
Honda  Hummer
Hummer  Hyundai
Hyundai  Infiniti
Infiniti  Isuzu
Isuzu  Iveco
Iveco  Jaguar
Jaguar  Jeep
Jeep  Kia
Kia  Lancia
Lancia  Land Rover
Land Rover  Lexus
Lexus  Lincoln
Lincoln  Mazda
Mazda  Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz  Mercury
Mercury  MINI
MINI  Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi  Nissan
Nissan  Oldsmobile
Oldsmobile  Opel
Opel  Peugeot
Peugeot  Pontiac
Pontiac  Porsche
Porsche  Plymouth
Plymouth  Ram
Ram  Renault
Renault  Rover
Rover  Saab
Saab  Saturn
Saturn  Scion
Scion  SEAT
SEAT  Skoda
Skoda  Smart
Smart  SsangYong
SsangYong  Subaru
Subaru  Suzuki
Suzuki  Tesla
Tesla  Toyota
Toyota  Vauxhall
Vauxhall  Volkswagen
Volkswagen  Volvo
Volvo
Why do fuses burn out?
They burn out due to exceeding the permitted load in the electrical circuit. This may be due to the connection of additional equipment, short circuits, wear and tear or jamming of motors, and other causes.
How to check the fuse?
The easiest method is to visually inspect the fuse – if the fusible element inside the fuse is damaged, the fuse has blown.
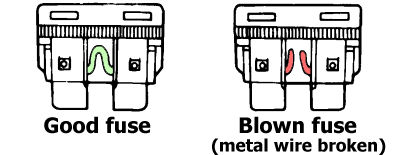
You can also check it with a multimeter. In “continuity mode”, it will emit a sound signal when the probes touch both of the fuse’s contact points if the fuse is good.
Circuit Breakers
The circuit breakers will reset themselves and allow the electrical parts to work again once the overload on the circuit is removed. If the circuit breakers continue to cut off electricity,
have your vehicle’s electrical system checked.
Relays
Relays are devices that receive signals from components or systems. After receiving signals, relays transfer these signals to activate or deactivate other components or systems.
